- FMA
- The Fabricator
- FABTECH
- Canadian Metalworking
Categories
- Additive Manufacturing
- Aluminum Welding
- Arc Welding
- Assembly and Joining
- Automation and Robotics
- Bending and Forming
- Consumables
- Cutting and Weld Prep
- Electric Vehicles
- En Español
- Finishing
- Hydroforming
- Laser Cutting
- Laser Welding
- Machining
- Manufacturing Software
- Materials Handling
- Metals/Materials
- Oxyfuel Cutting
- Plasma Cutting
- Power Tools
- Punching and Other Holemaking
- Roll Forming
- Safety
- Sawing
- Shearing
- Shop Management
- Testing and Measuring
- Tube and Pipe Fabrication
- Tube and Pipe Production
- Waterjet Cutting
Industry Directory
Webcasts
Podcasts
FAB 40
Advertise
Subscribe
Account Login
Search
NIMS releases findings based on 50 years of measuring metal wear and tear
- February 5, 2020
- News Release
- Metals/Materials
For the past 50 years researchers at the National Institute for Materials Science (NIMS) have been conducting detailed short- and long-term testing of a variety of structural materials manufactured in Japan to ensure they can withstand long-term stresses. Now NIMS scientists have reviewed this data in the journal Science and Technology of Advanced Materials, summarizing the institute's major findings.
In 1966 NIMS' predecessor, the National Research Institute for Metals, launched its creep data sheet project. The aim of this project was to determine the stress required to rupture heat-resistant steels and alloys in 100,000 hours (about 11.4 years) at high temperatures. This creep rupture strength data was initially needed to determine the allowable stresses metals could be exposed to in power plants. More recently, however, this data has been used to assess how much longer power plant parts have before they begin to wear and tear.
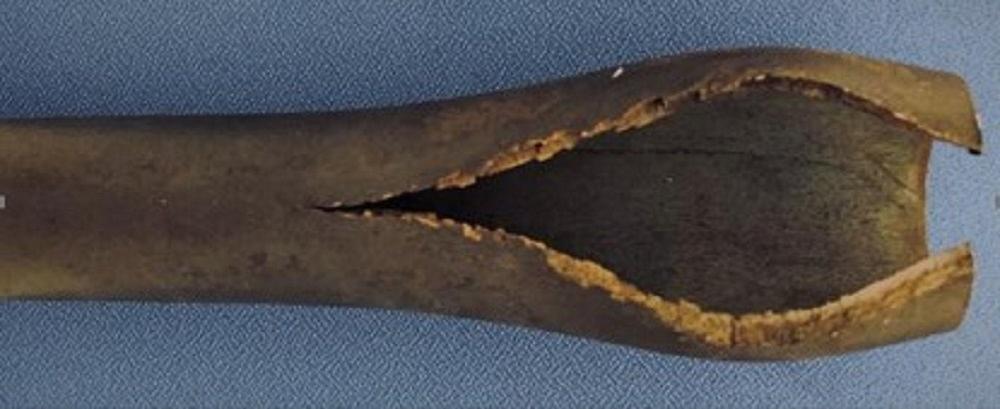
In 1978 NIMS also began assembling what has become a huge database of fatigue properties of structural materials used in numerous industries, including automobiles and aircrafts. Fatigue describes how cracks propagate in a metal over time. Fatigue tests involve placing a metal sample under repetitive loads, called cycles, to see how long it takes for a crack to develop and propagate. These tests are conducted at room temperature and high temperatures. Samples are exposed to a relatively small number of cycles (about 10 million) or up to 10 billion cycles, lasting for several years.
NIMS data has revealed that the long-term creep strength of materials varies and that scientists need to choose the type of analysis method for creep rupture data according to the type of material. How creep happens in materials during testing not only depends on the amount of stress applied, but also on the temperature conditions. The researchers have found that materials react differently to varying temperature depending on their chemical composition, the amounts of minor elements in them, and the crystal grain size. Ferritic heat-resistant steels, which are used commonly in thermal power plants, were found to have very long-term, inherent creep strength. But this creep strength depends on the amount of minor solutes present in the steel.
Fatigue limits, on the other hand, are affected by a metal's tensile strength and hardness. NIMS scientists have found that some metals can last for an incredibly long time without forming cracks as long as they are constantly exposed to room temperatures. These same metals, however, would eventually form cracks if exposed to the same stress but at high temperature.
subscribe now

The Fabricator is North America's leading magazine for the metal forming and fabricating industry. The magazine delivers the news, technical articles, and case histories that enable fabricators to do their jobs more efficiently. The Fabricator has served the industry since 1970.
start your free subscription- Stay connected from anywhere

Easily access valuable industry resources now with full access to the digital edition of The Fabricator.

Easily access valuable industry resources now with full access to the digital edition of The Welder.

Easily access valuable industry resources now with full access to the digital edition of The Tube and Pipe Journal.
- Podcasting
- Podcast:
- The Fabricator Podcast
- Published:
- 04/16/2024
- Running Time:
- 63:29
In this episode of The Fabricator Podcast, Caleb Chamberlain, co-founder and CEO of OSH Cut, discusses his company’s...
- Industry Events
16th Annual Safety Conference
- April 30 - May 1, 2024
- Elgin,
Pipe and Tube Conference
- May 21 - 22, 2024
- Omaha, NE
World-Class Roll Forming Workshop
- June 5 - 6, 2024
- Louisville, KY
Advanced Laser Application Workshop
- June 25 - 27, 2024
- Novi, MI