- FMA
- The Fabricator
- FABTECH
- Canadian Metalworking
Categories
- Additive Manufacturing
- Aluminum Welding
- Arc Welding
- Assembly and Joining
- Automation and Robotics
- Bending and Forming
- Consumables
- Cutting and Weld Prep
- Electric Vehicles
- En Español
- Finishing
- Hydroforming
- Laser Cutting
- Laser Welding
- Machining
- Manufacturing Software
- Materials Handling
- Metals/Materials
- Oxyfuel Cutting
- Plasma Cutting
- Power Tools
- Punching and Other Holemaking
- Roll Forming
- Safety
- Sawing
- Shearing
- Shop Management
- Testing and Measuring
- Tube and Pipe Fabrication
- Tube and Pipe Production
- Waterjet Cutting
Industry Directory
Webcasts
Podcasts
FAB 40
Advertise
Subscribe
Account Login
Search
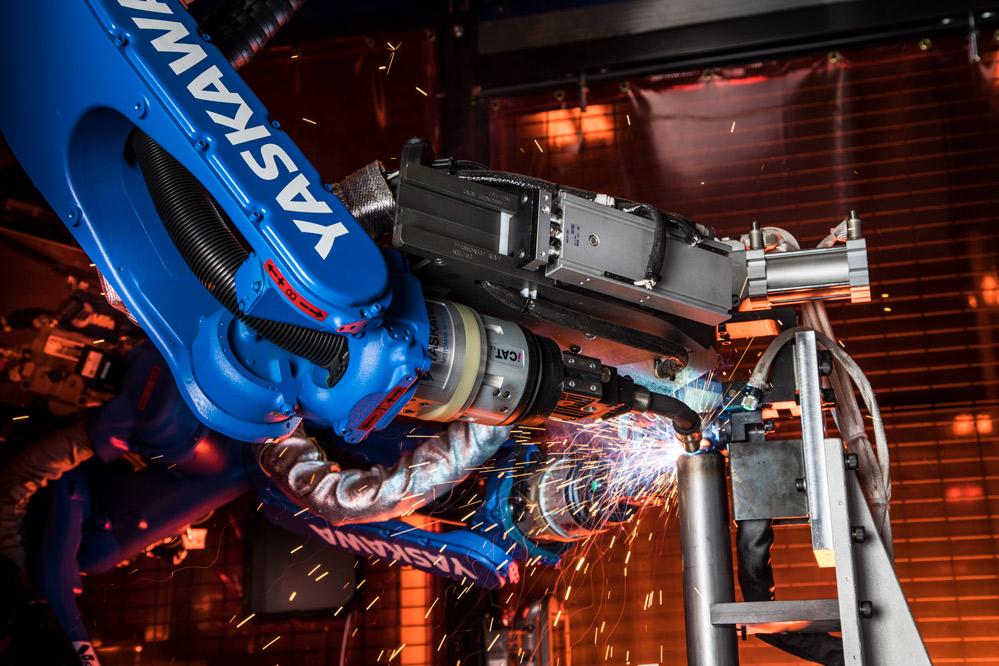
Robotic welding system helps chassis supplier exceed OEM requirements for safety-critical welds
- April 10, 2019
- News Release
- Shop Management
Situation: BWI Group, Kettering, Ohio, a joint venture of Shougang Corp. and Beijing Fangshan State & Asset Management Co. Ltd., is a chassis supplier and manufacturer of vehicle brake and suspension systems for the global transportation market.
Shortly after the company’s founding, BWI and its subsidiaries acquired the Chassis Division of Delphi Corp., which was formed years earlier by General Motors. This auto industry experience and resources helped the company establish itself as a technology provider for automotive, motorcycle, and specialty vehicle customers worldwide.
While BWI’s Validation and Test Development group performs fatigue or “life” tests on each component during the development process to ensure product safety, speed to market is equally vital to company success. For these reasons, weld quality and cycle time are key areas of focus on the production floor.
In need of a second opinion about what equipment combination to use for the incorporation of a GMAW system that would exceed original equipment manufacturer (OEM) requirements for safety-critical welds on thin-wall suspension components, the company reached out to Miller Electric Mfg. LLC, Appleton, Wis. Specifically, BWI wanted Miller Electric’s opinion on the ability to ensure OEMs that nonconforming parts could be contained from production flow and that safety-critical welds were within specified limits.
After initial meetings with BWI Group, Miller Electric weld and automation specialists suggested that Yaskawa America Inc.—Motoman Robotics Division be consulted about designing a customized robotic system.
Resolution: BWI’s engineering team agreed to observe a joint demonstration by the Yaskawa Motoman® and Miller Electric team. Several weeks before the presentation date, BWI Group supplied Yaskawa Motoman with the welding brackets and tube assemblies to be welded. A team of automation engineers and welding experts, from both Yaskawa Motoman and Miller Electric, integrated technology and developed procedures for the application.
Fixturing to prevent components from being loaded incorrectly was designed and built on-site, and an expert from Hobart Filler Metals, Troy, Ohio, was consulted to discuss alternative wire types. A general-purpose welding wire, ER70S0-3 0.035 (90/10 gas) solid wire, was chosen.
After the welding demonstration, BWI moved forward with the customization of four ArcWorld® 1200 workcells to fulfill immediate application needs at its production facility in Chihuahua, Mexico. Each customized system features two Motoman MH12 6-axis robots configured for arc welding to support the weight of a Vitronic laser seam inspection system to monitor weld size, porosity, undercut, and crater fill. Every welding robot includes a Miller Auto-Continuum™ 500 weld package and a Miller Coolmate™ 4 water circulator.
To enable each robot to verify that short structural welds are performed within established limits, Miller Electric’s Insight Centerpoint ™ arc data monitoring software is configured to monitor amperage and voltage and integrated with the laser seam inspection system. This configuration helps the robotic welding system track nonconforming parts unloaded by the operator. An HMI operator station with pedestal mount provides a graphic display that workcell operators use to monitor the weld sequence and clamp status for each weldment.
Each cell includes two MHT-185 headstock/tailstock positioners, one Binzel TCS-Reamer, one MSR-355 rotary positioner, and one hard-stop kit. The headstock/tailstocks feature the patented MotoMount ™ fixture mounting system to help simplify tooling and reduce stress on positioner bearings. Yaskawa’s MotoCal™ software tool is integrated on each robot to help improve positioning accuracy, tool control point, and tool posture.
Since summer 2018, the robotic workcells have been used at the Mexico facility to weld a variety of suspension components for high-end struts and shocks for multiple vehicle manufacturers. Each two-station system operates three shifts, five days a week. While seam tracking has added to the cycle time of each part, the workcells have eliminated rework, improving overall cycle time.
And BWI is achieving the high weld quality demanded by its customers, exceeding OEM requirements for safety-critical welds.
Yaskawa Motoman
subscribe now

The Fabricator is North America's leading magazine for the metal forming and fabricating industry. The magazine delivers the news, technical articles, and case histories that enable fabricators to do their jobs more efficiently. The Fabricator has served the industry since 1970.
start your free subscription- Stay connected from anywhere

Easily access valuable industry resources now with full access to the digital edition of The Fabricator.

Easily access valuable industry resources now with full access to the digital edition of The Welder.

Easily access valuable industry resources now with full access to the digital edition of The Tube and Pipe Journal.
- Podcasting
- Podcast:
- The Fabricator Podcast
- Published:
- 04/30/2024
- Running Time:
- 53:00
Seth Feldman of Iowa-based Wertzbaugher Services joins The Fabricator Podcast to offer his take as a Gen Zer...
- Industry Events
Pipe and Tube Conference
- May 21 - 22, 2024
- Omaha, NE
World-Class Roll Forming Workshop
- June 5 - 6, 2024
- Louisville, KY
Advanced Laser Application Workshop
- June 25 - 27, 2024
- Novi, MI
Precision Press Brake Certificate Course
- July 31 - August 1, 2024
- Elgin,