- FMA
- The Fabricator
- FABTECH
- Canadian Metalworking
Categories
- Additive Manufacturing
- Aluminum Welding
- Arc Welding
- Assembly and Joining
- Automation and Robotics
- Bending and Forming
- Consumables
- Cutting and Weld Prep
- Electric Vehicles
- En Español
- Finishing
- Hydroforming
- Laser Cutting
- Laser Welding
- Machining
- Manufacturing Software
- Materials Handling
- Metals/Materials
- Oxyfuel Cutting
- Plasma Cutting
- Power Tools
- Punching and Other Holemaking
- Roll Forming
- Safety
- Sawing
- Shearing
- Shop Management
- Testing and Measuring
- Tube and Pipe Fabrication
- Tube and Pipe Production
- Waterjet Cutting
Industry Directory
Webcasts
Podcasts
FAB 40
Advertise
Subscribe
Account Login
Search
Safeguarding tube benders with laser scanners
Noncontact, minimal-interference method ideal for large, irregularly shaped areas
- By Steve Aamodt
- February 13, 2007
- Article
- Tube and Pipe Fabrication
The optimal safeguarding equipment for each tube bending operation varies, depending on the application, the identified tasks, the risk level, and the applicable regulations and standards. Typically, tube bending machine safeguarding is needed in front of the machine where the tube is bent (point-of-operation); around its perimeter; and behind the machine, where the tube is fed.
Laser scanners, light curtains, and safety mats comprise many of the possible solutions for safeguarding tube bending machines. In addition, barrier guards and awareness devices, such as alarms, may be required to ensure the effectiveness of the safeguarding system (see Barrier Guards Sidebar).
Section 8.2 ANSI B11.15—2001 states that safeguarding devices, such as electro-optical devices, light curtains, laser scanners, and safety mats, must detect the presence of personnel, stop the hazardous motion immediately, and prevent initiation of further hazardous motion. In addition, they must require reinitiation of the normal actuating control before the machine starts up again.
Optical electronic devices, such as laser scanners, are presence-sensing devices that are suitable for area safeguarding.
Minimizing Interference
A laser scanner offers several advantageous features. First, because it is a noncontact method, it minimizes interference with the machine operation. Second, because it mounts at the foot of the machine and out of the way of the tube bending action, it allows full access to the work area.
Although laser scanning can be used in any area shape, it is especially cost-effective for irregularly shaped areas and areas bigger than the largest standard-sized safety mat (4 feet by 6 ft., typically). Protecting an area larger than 4 ft. by 6 ft. with safety mats would require purchasing more than one mat, and protecting an irregularly shaped area with safety mats means the safety mats must be customized.
| Barrier Guards |
Fixed Guards/BarrierAdvantages
Disadvantages
|
Adjustable Guards/BarriersAdvantages
Disadvantages
|
Interlocked Guards/BarriersAdvantages
Disadvantages
|
When laser scanners are used to guard irregularly shaped areas, shop floor space may be saved because the protective zone can be specified exactly, unlike perimeter light curtains, which can be arranged only in a rectangular shape around the hazard.
Another cost issue with safety mats is that they can become contaminated with oil, grease, and lubricants common in fabrication shops. Also, they can be worn by forklifts and other machinery.
Because laser scanning does not require physical handling, it does not expose operators to carpal tunnel syndrome and other repetitive stress injuries that may occur when using two-handed controls as the safeguarding method.
However, laser scanning does not offer protection for flying parts, such as barrier guards do. Also, it should not be used on machines that cannot be stopped quickly enough to prevent injuries from occurring.
How a Laser Scanner Operates
Safety categories defined by the European Committee for Standardization (CEN) EN 954-1 are B, 1, 2, 3, and 4—with 4 being the most stringent. Most laser scanners are classified as a Category 3 safety device. According to the standard, Category 3 safety-related parts of controllers and their safety devices, as well as their components, must be designed, built, selected, assembled, and combined in accordance with the applicable standard in such a way that they can withstand the effects to be expected. Category 3 safety-related parts must be designed in such a way that a single failure in any one of these parts does not lead to the loss of the safety function and, whenever feasible, the single failure is detected.
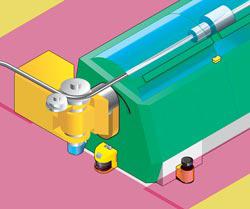
A laser beam is transmitted to form a detection area. When an object is detected, the laser scanner determines the distance between itself and the object within its sensing area and compares the distance to the object with the programmed safety zone and warning zone.
Two zone types are user-defined (see lead image)—a safety zone (also called the protective zone or the protective field) with a maximum radius and a warning zone (also known as the warning field) with a maximum radius.
If an operator enters the warning zone, the laser scanner provides an output that can be integrated with an alarm or a visual indicator. If the operator violates the safety zone, an output signal is generated to initiate a safety stop of the hazardous motion of the machine.
Programming a Laser Scanner
Several parameters must be identified to program the laser scanner properly:
- Maximum range
- Minimum objective sensitivity within safeguarding range
- Maximum field of view in degrees
- Tolerance in the range measurement
- Detection capabilities (object reflectivity versus distance)
Laser scanning is relatively simple to program. Most laser scanners come with Microsoft Windows®-based software that includes wizard tools for configuring the laser scanner parameters. The software also includes simple drawing tools to allow operators to draw their warning and safety zones. Once the integrator/user parameters and detection zones have been selected in the software, the configuration is downloaded to the device.
About the Author
Steve Aamodt
6900 W. 110th St.
Minneapolis, MN 55438
952-941-6780
subscribe now

The Fabricator is North America's leading magazine for the metal forming and fabricating industry. The magazine delivers the news, technical articles, and case histories that enable fabricators to do their jobs more efficiently. The Fabricator has served the industry since 1970.
start your free subscription- Stay connected from anywhere

Easily access valuable industry resources now with full access to the digital edition of The Fabricator.

Easily access valuable industry resources now with full access to the digital edition of The Welder.

Easily access valuable industry resources now with full access to the digital edition of The Tube and Pipe Journal.
- Podcasting
- Podcast:
- The Fabricator Podcast
- Published:
- 04/16/2024
- Running Time:
- 63:29
In this episode of The Fabricator Podcast, Caleb Chamberlain, co-founder and CEO of OSH Cut, discusses his company’s...
- Industry Events
16th Annual Safety Conference
- April 30 - May 1, 2024
- Elgin,
Pipe and Tube Conference
- May 21 - 22, 2024
- Omaha, NE
World-Class Roll Forming Workshop
- June 5 - 6, 2024
- Louisville, KY
Advanced Laser Application Workshop
- June 25 - 27, 2024
- Novi, MI