Vice President, Safety and Health
- FMA
- The Fabricator
- FABTECH
- Canadian Metalworking
Categories
- Additive Manufacturing
- Aluminum Welding
- Arc Welding
- Assembly and Joining
- Automation and Robotics
- Bending and Forming
- Consumables
- Cutting and Weld Prep
- Electric Vehicles
- En Español
- Finishing
- Hydroforming
- Laser Cutting
- Laser Welding
- Machining
- Manufacturing Software
- Materials Handling
- Metals/Materials
- Oxyfuel Cutting
- Plasma Cutting
- Power Tools
- Punching and Other Holemaking
- Roll Forming
- Safety
- Sawing
- Shearing
- Shop Management
- Testing and Measuring
- Tube and Pipe Fabrication
- Tube and Pipe Production
- Waterjet Cutting
Industry Directory
Webcasts
Podcasts
FAB 40
Advertise
Subscribe
Account Login
Search
Safety tips for laser and plasma cutting
Specific safety measures and PPE are essential for operators in these environments
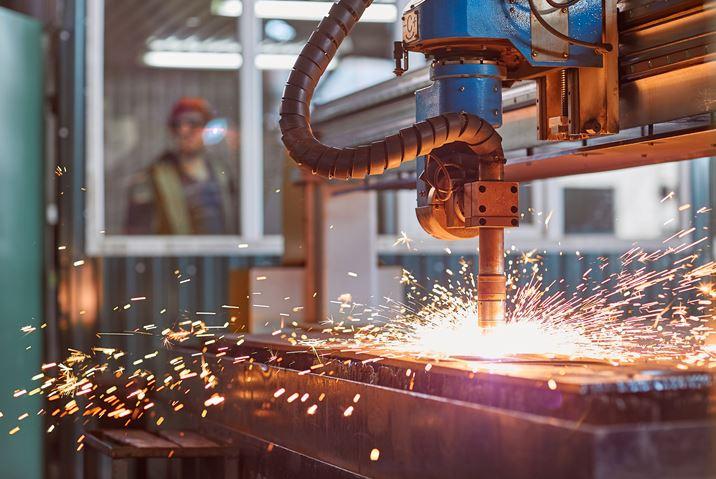

Operators must adhere to specific safety measures and use appropriate PPE to mitigate the inherent risks associated with laser and plasma cutting. Sergii Kolesnikov/iStock/Getty Images Plus
Laser and plasma cutting technologies have revolutionized the manufacturing and fabrication industries by providing precise and efficient cutting of a wide variety of materials. Laser cutting employs a high-powered laser beam, focused through optics, to melt, burn, or vaporize material. Plasma cutting, on the other hand, uses a plasma torch that creates a high-velocity jet of ionized gas to cut through electrically conductive metals.
Operators must adhere to specific safety measures and use personal protective equipment (PPE) to mitigate the inherent risks associated with these cutting technologies, including exposure to high temperatures, hazardous gases, and intense light emissions. A comprehensive approach to workplace safety and operator protection can help ensure worker safety in laser and plasma cutting operations.
Workplace Hazard Assessment
Conducting a thorough workplace hazard assessment is essential for ensuring the safety of operators in laser and plasma cutting operations. This assessment should encompass several key points:
- Environmental and operating permits - Operators must verify that their cutting processes comply with local and environmental regulations. This may involve obtaining specific permits, such as fire marshal approvals, or adhering to local building codes to legally conduct their operations.
- Electrical hazards - Laser and plasma cutting machines require high levels of electricity. Operators must ensure that the electrical supply, including amperages, fuses, and breakers, is adequate for their equipment's demands.
- Gas supply hoses - Operators should routinely inspect hoses for leaks, holes, frays, or any form of damage that could pose a risk.
- Fire prevention - Given the high temperatures involved in cutting operations, maintaining a safe distance of at least 35 ft. from combustibles, flammables, oils, and greases is recommended. Fire extinguishers should be readily accessible, and equipment should be equipped with flashback protection to mitigate fire risks.
- PPE - The selection of PPE, particularly eye protection, is determined by the arc's temperature and the material being cut. Welding hoods with the appropriate shade level, typically a level 10 or 11 or greater, are necessary to protect operators' eyes. A safety professional or industrial hygienist can help assess and recommend the proper respiratory protection and exhaust systems. This is critical for preventing acute and chronic respiratory illnesses due to exposure to harmful fumes and dust generated during the cutting process.
Adherence to these guidelines helps ensure a safer working environment, minimizing the risk of injuries and health problems among operators.
Specific Safety Measures for Laser and Plasma Cutting
Following a comprehensive workplace hazard assessment, implementing specific safety measures tailored to laser and plasma cutting operations is critical for safeguarding operators and the workplace. These measures vary slightly between the two cutting technologies but share common principles of fire prevention, proper training, and heightened awareness.
Laser Cutting Safety:
- Operation and maintenance - Regular maintenance and operational checks are fundamental to laser cutting safety. Ensuring that all laser equipment is functioning correctly and that safety features are intact can prevent accidents. This includes checking laser alignment, the condition of the laser bed, and the proper operation of ventilation systems to remove hazardous fumes.
- Material safety - Operators must be aware of the specific hazards associated with the materials they are cutting. Some materials can emit toxic fumes when cut with a laser, necessitating adequate ventilation and respiratory protection. Additionally, reflective materials require special handling to prevent laser beam reflection, which can pose a risk to operators and equipment.
Plasma Cutting Safety:
- Electrical safety - Plasma cutters require careful handling because of their high electrical demand. Operators should ensure that all electrical connections are secure and that the equipment is properly grounded to prevent electrical shocks. Regular inspections for wear and tear on cables and connections are essential to maintain electrical safety.
Common Safety Measures for Both Technologies:
- Fire prevention and management - Both laser and plasma cutting operations should implement strict fire prevention strategies. This includes maintaining a clean work area that is free from combustible materials, as well as having fire extinguishers and fire blankets readily accessible. Establishing clear fire safety protocols and ensuring all staff are trained in these procedures are vital.
- Training - Comprehensive training programs are crucial for all operators. These programs should cover the safe operation of the equipment, emergency response procedures, and the correct use of PPE. Regular safety meetings also can help keep safety protocols front and center, ensuring all team members are aware of their responsibilities.
- Heightened awareness - Encouraging a culture of safety first, where every operator is aware of the potential hazards and knows how to mitigate them, is essential. This includes recognizing the signs of equipment malfunction, understanding the risks associated with different materials, and knowing how to respond in an emergency.
Personal Protective Equipment
Building on the foundation of specific safety measures, the selection and use of PPE are fundamental components in ensuring the safety of operators during laser and plasma cutting operations. Proper PPE not only protects against immediate dangers but also minimizes long-term health risks associated with these processes.
Eye Protection. The intensity of the arc and the type of material being cut determine the necessary level of eye protection. Operators should consult safety guidelines to select the appropriate shade for their specific cutting tasks.
Welding hoods equipped with the correct shade of lens are critical to prevent eye damage such as retinal burns and long-term vision impairment caused by the bright arc light. For plasma cutting, shades typically are level 10 to level 11, depending on the brightness of the plasma arc.
Respiratory Protection. Given the potential for hazardous fumes and dust generated during cutting operations, wearing the right respiratory protection is essential. Respirator selection should be based on a thorough hazard assessment of the materials being cut.
Safety professionals and industrial hygienists can offer invaluable assistance in choosing suitable respiratory equipment, whether it be disposable masks for lower-toxicity materials or full-face respirators for more hazardous conditions. General ventilation systems play a crucial role in complementing personal respirators, ensuring that operators are not exposed to harmful airborne particles.
Additional PPE. Beyond eye and respiratory protection, operators should don full protective clothing to shield against sparks, hot metal, and UV radiation. This includes:
- Flame-resistant garments - Cover as much exposed skin as possible in flame-resistant clothing to protect against burns and UV exposure.
- Gloves - Heat-resistant gloves are necessary to handle hot materials and protect against cuts and burns. The gloves should be durable yet flexible to maintain dexterity during operation.
- Footwear - Safety boots or shoes, preferably made from leather or another flame-resistant material, protect against falling objects, sparks, and h
Safeguarding the Future of Cutting Operations
The meticulous implementation of specific safety measures and the diligent use of PPE are indispensable for ensuring the safety of operators in laser and plasma cutting environments. These practices not only protect individuals from immediate hazards but also contribute to the long-term health and efficiency of the workforce.
As technology and workplace demands evolve, so must our commitment to safety practices and protocols. It is a collective call to action for continuous improvement in safety measures, encouraging a proactive rather than reactive approach to workplace safety.
About the Author
Herb Post
2300 W Sahara Ave. Suite 800
Las Vegas, NV 89102
subscribe now

The Fabricator is North America's leading magazine for the metal forming and fabricating industry. The magazine delivers the news, technical articles, and case histories that enable fabricators to do their jobs more efficiently. The Fabricator has served the industry since 1970.
start your free subscription- Stay connected from anywhere

Easily access valuable industry resources now with full access to the digital edition of The Fabricator.

Easily access valuable industry resources now with full access to the digital edition of The Welder.

Easily access valuable industry resources now with full access to the digital edition of The Tube and Pipe Journal.
- Podcasting
- Podcast:
- The Fabricator Podcast
- Published:
- 04/16/2024
- Running Time:
- 63:29
In this episode of The Fabricator Podcast, Caleb Chamberlain, co-founder and CEO of OSH Cut, discusses his company’s...
- Trending Articles
Tips for creating sheet metal tubes with perforations

Are two heads better than one in fiber laser cutting?

Supporting the metal fabricating industry through FMA

JM Steel triples capacity for solar energy projects at Pennsylvania facility

Omco Solar opens second Alabama manufacturing facility

- Industry Events
16th Annual Safety Conference
- April 30 - May 1, 2024
- Elgin,
Pipe and Tube Conference
- May 21 - 22, 2024
- Omaha, NE
World-Class Roll Forming Workshop
- June 5 - 6, 2024
- Louisville, KY
Advanced Laser Application Workshop
- June 25 - 27, 2024
- Novi, MI