President
- FMA
- The Fabricator
- FABTECH
- Canadian Metalworking
Categories
- Additive Manufacturing
- Aluminum Welding
- Arc Welding
- Assembly and Joining
- Automation and Robotics
- Bending and Forming
- Consumables
- Cutting and Weld Prep
- Electric Vehicles
- En Español
- Finishing
- Hydroforming
- Laser Cutting
- Laser Welding
- Machining
- Manufacturing Software
- Materials Handling
- Metals/Materials
- Oxyfuel Cutting
- Plasma Cutting
- Power Tools
- Punching and Other Holemaking
- Roll Forming
- Safety
- Sawing
- Shearing
- Shop Management
- Testing and Measuring
- Tube and Pipe Fabrication
- Tube and Pipe Production
- Waterjet Cutting
Industry Directory
Webcasts
Podcasts
FAB 40
Advertise
Subscribe
Account Login
Search
Measure constantly, build better with smart manufacturing technology
Advances in monitoring, analyzing, and reporting manufacturing events promise to improve results
- By Bill Frahm
- October 9, 2023
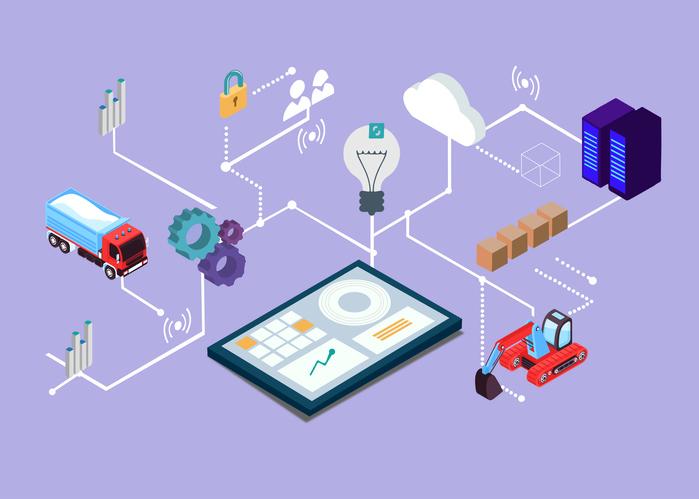
Today’s smart manufacturing technologies offer unprecedented opportunities to measure, identify, and correct inefficiencies across the entire supply chain, maintain equipment for optimal reliability, manage parameters for processing, and monitor logistical variables. reklamlar/DigitalVision Vectors
The adage “measure twice, cut once” remains an obvious and intuitive piece of advice. In modern manufacturing, it is challenging to measure each workpiece accurately before acting on it, especially since measure can mean dimensions, chemical properties, mechanical properties, wear, lubrication, age, and many more.
Smart manufacturing technologies offer useful and reliable tools to measure and analyze shop floor data to achieve manufacturing efficiency. And in an increasingly competitive world, manufacturing efficiency across the supply chain is a major component of sustainability, product quality, and overall business success.
The S Word
Let’s take a quick detour to define sustainability. It’s not a “woke” environmental concept. It’s about supporting manufacturing efficiency by adopting operations that reduce waste—and, coincidentally, don’t contaminate fish, game, and your neighbors. In fact, many of Henry Ford’s principles are in line with the principles of sustainability. Ford believed in reducing waste, gave to philanthropic organizations and believed that employees paid a fair wage would be more productive and loyal to his company.
And sustainability has financial rewards. Recent studies by Morningstar and MOrgan Stanley indicate that companies that use sustainable practices perform similarly to the broader market but perform better than others during a down market.
Correcting Inefficiencies
Today’s smart manufacturing technologies offer unprecedented opportunities to measure, identify, and correct inefficiencies across the entire supply chain, maintain equipment for optimal reliability, manage parameters for processing, and monitor logistical variables. This includes:
- Monitoring devices to collect data about events and states across a manufacturing process (IoT devices).
- Network technologies to integrate IoT devices and computing hardware.
- Robust storage technologies to store and manage large amounts of data.
- Software components to support sampling, descriptive analytics, predictive analytics, correlation, and causation analysis.
- Data analysts and subject matter experts able to collaborate to draw correct samples, identify anomalies and deal with outliers, and understand results and the proper courses of action.
While artificial intelligence is a possible component of smart manufacturing and is a promising emerging technology, its costs and risks are beyond the capabilities of most manufacturing organizations.
Parameters to Monitor
So what parameters can you potentially monitor, measure, and improve to ensure manufacturing efficiency across the supply chain?
Logistics:
- Demand prediction
- Sorting
- Planning
- Location reporting
- Route planning
Manufacturing:
- Input stock properties
- Optimal process paths
- Equipment lifecycle
- Condition based maintenance
- Dimensional analysis
- Design/simulation analysis
- Safety and incident analysis
- Energy usage
- Workforce scheduling
Customer experience:
- Warranty
- Delivery
- Customer satisfaction and issues
- Product lifecycle and durability
Collecting information allows for analyzing and reporting prior events, identifying correlation and cause/effect relationships, and predicting future events and results, and it allows immediate response to undesirable events before they become reliability, safety, or quality problems.
If you support the integrated use of smart manufacturing across the supply chain, the impact on sustainability, product quality, and profitability can truly change your manufacturing landscape.
subscribe now

The Fabricator is North America's leading magazine for the metal forming and fabricating industry. The magazine delivers the news, technical articles, and case histories that enable fabricators to do their jobs more efficiently. The Fabricator has served the industry since 1970.
start your free subscriptionAbout the Author

Bill Frahm
P.O. Box 71191
Rochester Hills, MI 48307
248-506-5873
- Stay connected from anywhere

Easily access valuable industry resources now with full access to the digital edition of The Fabricator.

Easily access valuable industry resources now with full access to the digital edition of The Welder.

Easily access valuable industry resources now with full access to the digital edition of The Tube and Pipe Journal.
- Podcasting
- Podcast:
- The Fabricator Podcast
- Published:
- 04/16/2024
- Running Time:
- 63:29
In this episode of The Fabricator Podcast, Caleb Chamberlain, co-founder and CEO of OSH Cut, discusses his company’s...
- Trending Articles
Tips for creating sheet metal tubes with perforations

Are two heads better than one in fiber laser cutting?

Supporting the metal fabricating industry through FMA

JM Steel triples capacity for solar energy projects at Pennsylvania facility

Omco Solar opens second Alabama manufacturing facility

- Industry Events
16th Annual Safety Conference
- April 30 - May 1, 2024
- Elgin,
Pipe and Tube Conference
- May 21 - 22, 2024
- Omaha, NE
World-Class Roll Forming Workshop
- June 5 - 6, 2024
- Louisville, KY
Advanced Laser Application Workshop
- June 25 - 27, 2024
- Novi, MI