- FMA
- The Fabricator
- FABTECH
- Canadian Metalworking
Our Publications
Categories
- Additive Manufacturing
- Aluminum Welding
- Arc Welding
- Assembly and Joining
- Automation and Robotics
- Bending and Forming
- Consumables
- Cutting and Weld Prep
- Electric Vehicles
- En Español
- Finishing
- Hydroforming
- Laser Cutting
- Laser Welding
- Machining
- Manufacturing Software
- Materials Handling
- Metals/Materials
- Oxyfuel Cutting
- Plasma Cutting
- Power Tools
- Punching and Other Holemaking
- Roll Forming
- Safety
- Sawing
- Shearing
- Shop Management
- Testing and Measuring
- Tube and Pipe Fabrication
- Tube and Pipe Production
- Waterjet Cutting
Industry Directory
Webcasts
Podcasts
FAB 40
Advertise
Subscribe
Account Login
Search
Volkswagen adopts binder-jet 3D-printing technology
- June 24, 2021
- News Release
- Additive Manufacturing
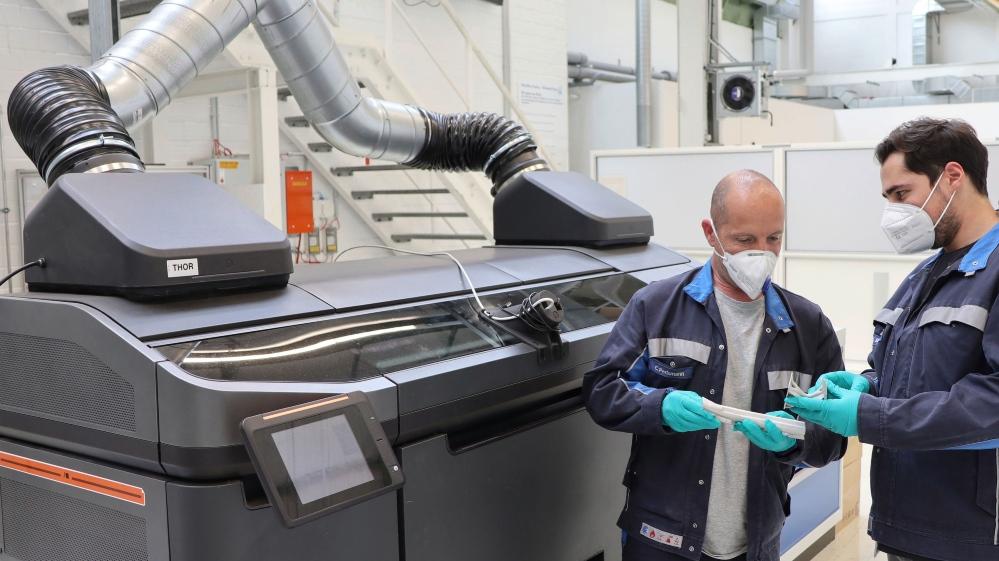

Volkswagen has partnered with Siemens and HP on the metal binder-jet 3D printing initiative. Volkswagen
Volkswagen is set to use binder-jet 3D printers to produce metal parts for cars built at its main plant, located in Wolfsburg, Germany.
With binder jetting, an industrial printhead selectively deposits binding agent on a metallic powder, which is then heated. The areas where the binding agent are deposited bond with previous and subsequent layers to form a 3D part.
Binder jetting reduces costs and increases productivity, according to a VW-issued press release, and yields lighter parts. For example, a binder-jetted component weighs roughly half as much as one made from steel sheet.
Volkswagen is currently the only carmaker using binder-jet 3D printing technology in production.
“Despite the ongoing challenges of the coronavirus pandemic, we’re continuing to work on innovation,” said Christian Vollmer, a member of the VW team responsible for production and logistics. “Together with our partners, we aim to make 3D printing even more efficient in the years ahead and more suitable for production-line use.”
The automaker’s partners in the initiative are Siemens AG, provider of the software, and HP Inc., which is supplying the 3D printers.
A key process step that has been worked on jointly by Siemens and VW is to optimize the positioning of components in the build chamber. Such optimization, or nesting, makes it possible to double the size of a build.
The first binder-jetted components—parts for the A-pillar of VW’s T-Roc convertible—currently are being certified. They weigh almost 50% less than conventional components made from steel sheet.
The carmaker plans to 3D-print up to 100,000 components annually at the Wolfsburg plant by 2025. Until now, the production of larger volumes was not sufficiently cost-effective. The new technology and the collaboration with Siemens and HP is expected to make production-line use of the technology economically viable.
Today, assorted 3D printing technologies are used at the Wolfsburg plant to manufacture plastic and metal components. Examples of plastic parts include prototypes of center consoles, door cladding, instrument panels, and bumpers. Among the printed metal components are intake manifolds, radiators, brackets, and support elements.
Volkswagen has 3D-printed more than 1 million components during the past 25 years.
- Podcasting
- Podcast:
- The Fabricator Podcast
- Published:
- 04/16/2024
- Running Time:
- 63:29
In this episode of The Fabricator Podcast, Caleb Chamberlain, co-founder and CEO of OSH Cut, discusses his company’s...
- Trending Articles
- Industry Events
16th Annual Safety Conference
- April 30 - May 1, 2024
- Elgin,
Pipe and Tube Conference
- May 21 - 22, 2024
- Omaha, NE
World-Class Roll Forming Workshop
- June 5 - 6, 2024
- Louisville, KY
Advanced Laser Application Workshop
- June 25 - 27, 2024
- Novi, MI